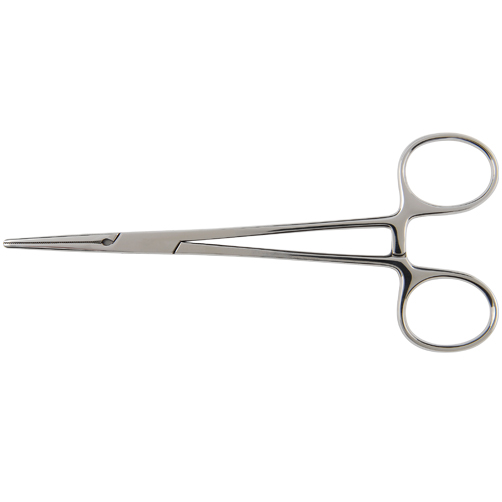
Hemostatic Forceps
Are you looking for hemostat forceps? We manufacture and supply hemostat forceps in curved and straight varieties,
Our high quality hemostat forceps are manufactured with precision to control bleeding by clamping and holding blood vessels so cauterization
or ligation can be performed. Our manufactured Hemostatic forceps are also used for fine tissue dissection and for holding small sutures.
Variations of Hemostatic Forceps available from our company included Rochester-Carmalt forceps, Crile forceps , Bull Dog Clamp
Hartman Mosquito
Hemostatic Forceps, Straight
Hartman Mosquito Hemostatic Forceps, Curved. Crile Forceps
Kelly Forcep
Towel Forcep
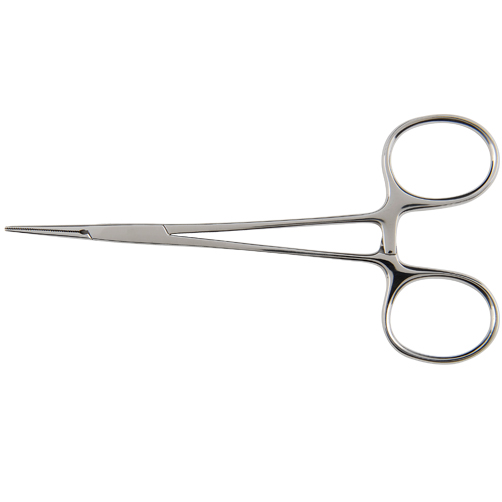
Mosquito Forceps
These are small, fine-tipped forceps used for holding delicate tissues and for precision tasks during surgery.
Mosquito forceps are delicate surgical instruments designed for precise work on small vessels and fine tissues. Here’s a detailed description of their characteristics and applications:
Characteristics:
Size and Delicacy:
Small and lightweight, making them ideal for intricate procedures.
Serrations:
The jaws are finely serrated along their entire length, providing a secure grip on tiny structures.
Jaw Shape:
Available with both straight and curved jaws to cater to different surgical needs.
Locking Mechanism:
Equipped with a ratchet lock that allows the forceps to maintain consistent pressure once closed.
Uses:
Clamping Small Blood Vessels:
Frequently used to clamp small blood vessels to control bleeding in delicate surgical areas.
Handling Fine Tissue:
Ideal for holding and manipulating fine or fragile tissues without causing significant damage.
Precision Work in Constrained Spaces:
Due to their small size, they are perfect for working in tight or confined surgical fields where precision is critical.
Micro-Surgeries and Pediatric Surgeries:
Commonly used in micro-surgeries and pediatric procedures where small anatomical structures need to be handled carefully.
Specific Surgical Applications:
General Surgery: Used for clamping small vessels and delicate tissues.
ENT (Ear, Nose, Throat) Surgery: Ideal for procedures involving fine structures in the head and neck.
Plastic Surgery: Employed in reconstructive procedures requiring precision.
Vascular Surgery: Utilized to manage small blood vessels.
Mosquito forceps are highly valued in the medical field for their ability to handle minute structures with great precision, making them indispensable for many specialized surgical procedures.
Crile forceps, often referred to as "hemostats," are surgical instruments used primarily to clamp blood vessels or tissue before ligation. Here are the key characteristics and uses of Crile forceps:
Size and Build:
Larger and less delicate than mosquito forceps.
Jaw Surface:
Features transverse serrations along the entire length of the jaw surface, which provides a secure grip on tissue or vessels.
Jaw Shape:
Available with either straight or curved jaws to accommodate different surgical needs and preferences.
Uses:
Occlusion of Small to Medium-Sized Vessels:
Commonly used to clamp off blood vessels during surgical procedures to prevent bleeding.
General Clamping:
Can be used to hold or manipulate tissue and other materials during surgery.
Crile forceps are versatile and widely used in various surgical disciplines due to their robust construction and effective clamping ability.

Kelly Forceps
These are curved, flat-tipped forceps used for clamping and holding tissues during surgical procedures.
Kelly forceps are surgical instruments commonly used for clamping large blood vessels or manipulating heavy tissue. They are part of the hemostatic forceps family and are frequently utilized in a wide range of surgical procedures.
Characteristics:
Size and Build:
Larger and more robust compared to some other hemostatic forceps like mosquito forceps.
Serrations:
Feature transverse serrations along part of the jaw, typically the distal half or two-thirds of the jaw surface. This partial serration differentiates Kelly forceps from Crile forceps, which have serrations along the entire length of the jaw.
Jaw Shape:
Available with both straight and curved jaws to accommodate different surgical tasks and surgeon preferences.
Locking Mechanism:
Equipped with a ratchet locking mechanism that allows the forceps to be locked in place, providing consistent pressure when clamped.
Uses:
Clamping Large Blood Vessels:
Often used to occlude larger blood vessels during surgical procedures to control bleeding.
Manipulating Heavy Tissue:
Suitable for holding and manipulating heavier tissues or structures, such as during the dissection of large masses or organ manipulation.
Tissue Retraction:
Used to retract tissues to provide better access to the surgical field.
General Clamping and Grasping:
Versatile in their application, Kelly forceps can be used for a variety of clamping and grasping needs in surgical settings.
Blunt Dissection:
Allis tissue forceps are specialized surgical instruments used to hold or grasp tissue. Here are the key uses and characteristics of Allis tissue forceps:
Characteristics: Teeth: Features multiple teeth at the tips (typically 4x5 or 5x6), which interlock when the forceps are closed, providing a strong grip on tissues.
Design: Has a ratchet locking mechanism that allows the forceps to stay securely closed once engaged.
Available in various lengths to suit different surgical needs. Uses: Grasping Tissue:
Commonly used to hold or grasp tissue firmly during surgical procedures. The toothed tips ensure that tissue is held securely, reducing the risk of slippage.
Holding Tissue for Removal: Used to grasp and hold tissue that is to be excised or removed, such as during the excision of tumors or other growths.
Manipulating Tissue: Helps in the manipulation of tissue during surgery, such as lifting or retracting tissues to improve access to the surgical site.
Holding Dense Tissue: Ideal for holding dense, slippery, or tough tissues like fascia, tendons, or the edges of surgical incisions. Assisting in Hemostasis:
Sometimes used to hold tissue that is being sutured or cauterized to achieve hemostasis (the stopping of bleeding). Specific Surgical Applications:
General Surgery: Used in procedures involving skin, muscle, and other tissues. Gynecological Surgery: Commonly used in surgeries involving the uterus, such as hysterectomies. Orthopedic Surgery: Used to handle tough connective tissues. Gastrointestinal Surgery: Utilized to grasp and manipulate the intestinal tissue. Allis tissue forceps are highly valued for their ability to hold tissue securely without causing significant damage, making them essential in various surgical procedures
Sometimes employed in blunt dissection techniques, where the forceps are used to separate tissue planes by pushing rather than cutting.
Specific Surgical Applications:
General Surgery: Commonly used for clamping blood vessels and manipulating tissue.
Gynecology: Utilized in procedures like hysterectomies to clamp blood vessels and manipulate uterine tissue.
Orthopedics: Employed in surgeries involving bones and joints to control bleeding and handle tough tissues.
Gastrointestinal Surgery: Used to manage bleeding and manipulate organs and tissues within the abdominal cavity.
Kelly forceps are essential tools in the surgical arsenal, valued for their ability to securely clamp larger structures and manage tissue effectively without causing excessive damage.
The manufacturing procedure for needle holder forceps involves several precise and controlled steps to ensure the final product meets the stringent requirements for surgical instruments. Here is an overview of the key stages in the manufacturing process:
1. Material Selection
Stainless Steel: High-grade stainless steel is commonly used due to its strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to be sterilized.
2. Forging
Heating: The stainless steel is heated to a high temperature to make it malleable.
Shaping: The heated metal is placed into a die and hammered or pressed into the rough shape of the needle holder forceps. This process is known as forging.
Cooling: The forged pieces are allowed to cool slowly to ensure uniform structure and strength.
3. Machining
Trimming: Excess material from the forging process is trimmed away to refine the shape.
Milling and Drilling: Precision machines are used to mill and drill the necessary features, such as the jaw serrations, box lock, and ratchet mechanism.
Grinding: The surface of the forceps is ground to achieve the desired smoothness and shape. This step ensures that the jaws align correctly and the ratchet mechanism works smoothly.
4. Heat Treatment
Hardening: The forceps are subjected to a controlled heating and cooling process to harden the steel, enhancing its durability and strength.
Tempering: A subsequent tempering process reduces the brittleness imparted by hardening and adds toughness.
5. Assembly
Fitting: Components such as the two arms of the forceps, the box lock, and the ratchet are carefully fitted together. Precision is crucial to ensure proper function.
Riveting or Welding: The parts are permanently joined, typically using riveting or welding techniques.
6. Finishing
Polishing: The entire instrument is polished to a high sheen, removing any surface imperfections. This also enhances its resistance to corrosion and makes it easier to clean.
Electroplating (Optional): Some needle holders may undergo electroplating to add an additional protective layer.
7. Quality Control
Inspection: Each needle holder forceps undergoes thorough inspection to ensure it meets all specifications for size, shape, alignment, and function.
Testing: Functional tests, including checking the grip strength, ratchet mechanism, and jaw alignment, are performed.
8. Cleaning and Sterilization
Cleaning: The forceps are meticulously cleaned to remove any manufacturing residues.
Sterilization: The instruments are sterilized to ensure they are free from any microbial contamination before packaging.
9. Packaging
Sterile Packaging: The forceps are packaged in sterile conditions, typically in sealed, sterile pouches or trays.
Labeling: Each package is labeled with relevant information such as the type of instrument, manufacturer, and sterilization date.
10. Distribution
The packaged needle holder forceps are distributed to hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities.
By adhering to these detailed steps, manufacturers ensure that needle holder forceps are reliable, durable, and safe for use in surgical procedures.
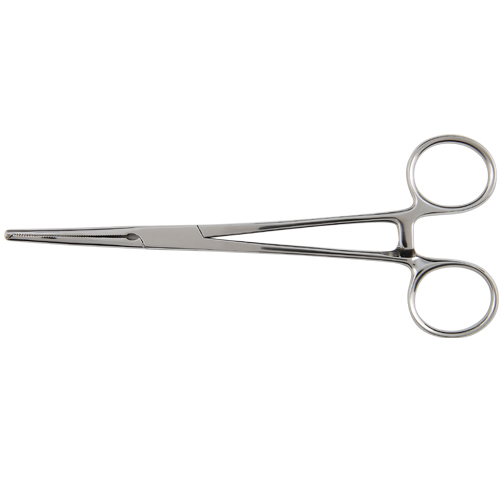
Kocher Artery Forceps
These are curved, blunt-tipped forceps used for holding and manipulating tissues during surgery.
The production of sponge holding forceps involves a series of precise steps to ensure the instrument is of high quality and suitable for surgical use.
1. Material Selection
High-Quality Stainless Steel: Chosen for its durability, resistance to rust, and ease of sterilization.
2. Initial Forging
Heating the Metal: The stainless steel is heated until it becomes malleable.
Shaping: The heated steel is placed in a mold and hammered or pressed into the basic shape of the forceps. This process is called forging.
Cooling: The forged components are gradually cooled to stabilize their structure.
3. Precision Machining
Cutting and Trimming: Excess material from the forging is removed to refine the shape of the forceps.
Detailed Shaping: Precision machining tools are used to create the detailed features of the forceps, such as the jaws, box lock, and ratchet mechanism.
Grinding: The forceps are ground to achieve the required smoothness and precise fit of components.
4. Heat Treatment
Hardening Process: The forceps are heated and then rapidly cooled to increase their hardness and strength.
Tempering: The hardened forceps are reheated to a lower temperature and then cooled again to reduce brittleness and enhance toughness.
5. Assembly
Component Fitting: The various parts of the forceps, including the two arms, the box lock, and the ratchet mechanism, are carefully assembled.
Joining Techniques: The components are permanently joined together using techniques such as riveting or welding, ensuring a secure fit.
6. Surface Finishing
Polishing: The assembled forceps are polished to a high shine, which not only improves appearance but also enhances corrosion resistance and cleanliness.
Optional Coating: An additional protective coating, such as electroplating, may be applied to further enhance durability.
7. Quality Assurance
Inspection: Each forceps is thoroughly inspected to ensure it meets precise specifications for alignment, functionality, and overall quality.
Functional Testing: Tests are conducted to verify the grip strength, alignment of the jaws, and operation of the ratchet mechanism.
8. Cleaning and Sterilization
Detailed Cleaning: The forceps are meticulously cleaned to remove any residues from the manufacturing process.
Sterilization Process: The cleaned forceps are sterilized to eliminate any microbial contamination, making them safe for surgical use.
9. Packaging
Sterile Packaging: The sterilized forceps are packaged in sterile conditions, typically in sealed pouches or trays to maintain sterility.
Labeling: Each package is labeled with necessary information, including the type of instrument, manufacturer details, and sterilization date.
10. Distribution
Shipping: The packaged forceps are then distributed to medical facilities such as hospitals and clinics.
By following these detailed steps, manufacturers ensure that sponge holding forceps are reliable, durable, and safe for surgical applications.

Kocher Artery Forceps
These are curved, blunt-tipped forceps used for holding and manipulating tissues during surgery.
Contact Us
Do you have further Questions or want a customized product? Our team is here to help with additional information on our products, grant proposals, orders and more. Contact us by Email or whatsapp.!

Phone: +00923338600692
Email: info@hemostatic-forceps.com
Whatsapp 923338600692 or leave me a note: